In our digital-first era, SEO is crucial for making sure your content reaches its audience. With vast amounts of information online, optimizing your content helps it stand out and rank well in search results.
Technical SEO is essential for ensuring that your content not only reaches its audience but also performs optimally across devices.
Technical SEO, content strategy, and link-building strategies all work together to help your pages rank higher in search results.
In this post, you’ll learn the fundamentals of technical SEO, from conducting an initial site audit to crafting a targeted optimization plan.
Let’s dive in!
Content
- What is Technical SEO.
- Technical SEO Fundamentals.
- Understanding Crawlability and optimizing for it.
- Understanding Rendering and optimizing for it.
- Understanding Indexability and optimizing for it.
- Understanding Rankability and optimizing for it.
- Understanding Clickability and optimizing for it.
What Is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO is essential for enhancing your website’s visibility and usability, making it easier for search engines to find, understand, and index your content.
It goes beyond search engine optimization as it creates a smoother user experience by improving mobile accessibility, speeding up page load times, and organizing site architecture.
This approach not only boosts visibility but can also make or break your SEO performance.
- If pages aren’t accessible to search engines, they won’t appear in search results—regardless of the value of your content—leading to lost traffic and potential revenue.
- Confirmed ranking factors like site speed and mobile-friendliness also play a role; if pages load slowly or don’t function well on mobile, users may leave, signaling to search engines that your site may not provide a positive experience, which can impact rankings.
When done right, technical SEO can greatly enhance your search visibility and overall performance.
To understand technical SEO better, let’s explore SEO in phases
Simplifying Technical SEO
Technical SEO can be overwhelming, so it’s helpful to break it down into manageable pieces.
There are 5 main categories in Technical SEO that best describe the way to conduct an audit, which are:
But, before you begin learning about these, you need to know SEO fundamentals.
Technical SEO Fundamentals
Audit your Domain
Your domain is the web address that users enter to visit your site, like sarahfkambou.com. It significantly influences how easily people can find you in search results and provides a consistent identity for your site.
By choosing a preferred domain, you indicate to search engines whether you want the www or non-www version of your site to appear in search results. For example, if you prefer (http://www.yourwebsite.com), search engines will prioritize that version and redirect all users there. If you don’t specify a preference, search engines may see both versions as separate sites, which can dilute your SEO efforts. A study by SE Ranking highlights that many sites still face issues due to a lack of redirects between the www and non-www versions, leading to duplicate content and hindering SEO performance.
If you want to set your preferred domain, you can do so through canonical tags (which we’ll discuss soon). No matter what, ensure that all variations, including www, non-www, http, and index.html, redirect to your chosen version.
SSL Certificate
Have you noticed that some websites use “http” instead of “https”, and some websites say “not secured” with a padlock icon in the address bar?
Well, you might have come across the term SSL, or Secure Sockets Layer, before—it’s quite significant!
SSL provides a protective layer between the web server (which handles online requests) and the browser, enhancing your site’s security. This means that when users submit sensitive information, like payment or contact details, the risk of that data being intercepted is significantly reduced.
Search engines favor secure sites, and Google stated as early as 2014 that SSL would be a ranking factor. Therefore, it’s crucial to set the SSL version of your homepage as your preferred domain.
Luckily several hosting platforms offer SSL for free in their plans. But some pages may not be secured so make sure to migrate any non-SSL pages from http to https!
Optimize Page Speed
Have you ever waited for a page to load for over 5 seconds?
Most people do not want to wait for a page to load. In fact, it increases your bounce rate which is awful for rankings.
So, use these few tips to improve your page load time:
- Regularly redirect: Use plugins like Redirection – WordPress plugin | WordPress.org to streamline redirects. Make sure to upload your new sitemap to Google Search Console.
- Compress all media: When you compress your images, they take up less space and load faster.
- Limit Plugins: Use only essential plugins, as outdated plugins may have security vulnerabilities that make your site susceptible to attacks. Use cache plugins to create a static version of your site.
- Content Distribution Network (CDN): CDNs reduce the distance data must travel, as they store copies of your website across multiple geographical locations. By delivering your site based on the user’s location, CDNs ensure faster loading times for visitors.
Now that you have those covered, we can move on to he good stuff!
Crawlability Optimization
Crawling is a crucial aspect of how search engines operate, as it refers to how easily search engine bots can discover and navigate through your website’s pages to discover new content. For instance, when I publish new blog posts, I add them to my main blog page, enabling search engines like Google to find these recently added links during their next crawl.
This process of crawlability serves as the foundation of your technical SEO strategy, allowing search bots to gather essential information about your site. If these bots are blocked from accessing your pages, they cannot index or rank your content. Therefore, the first step in implementing a successful technical SEO strategy is to ensure that all your important pages are easily accessible and navigable.
Here are some points to focus on:

1. XML Sitemap Creation
Create an XML Sitemap which is essential for guiding search bots through your website’s structure, allowing them to easily find and crawl your web pages. Think of it as a roadmap for search engines.
Sitemap Types
– XML Sitemap: Primarily designed for search engines, this format includes important metadata about your pages, such as the last modified date, priority, and frequency of updates. It helps search engines index your site more effectively.
– HTML Sitemap: This type is intended for users, providing a structured view of your website’s content. It can enhance user experience by helping visitors navigate your site easily.
Once your XML sitemap is complete, submit it to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools to ensure search engines can efficiently crawl your pages. This submission enhances the discoverability of new content and helps search engines prioritize which pages to index. A well-maintained sitemap also reduces the risk of orphaned pages—those not linked to by other pages—remaining unindexed.
2. Use Robots.txt
When a web robot crawls your site, it first checks the robots.txt file, also known as the Robot Exclusion Protocol. This file specifies which web crawlers are allowed or disallowed from accessing certain sections or pages of your site. If you want to prevent specific pages from being indexed, you can use the `noindex` robots meta tag.
Key Points:
- Blocking Malicious Bots: You might want to block harmful bots that scrape content or spam forums. In this case, the robots.txt file acts as a protective barrier, keeping these bad bots away from your site.
- Crawling and Indexing: Search bots crawl your site to gather information and identify keywords, helping to match your pages with relevant search queries. However, it’s important to manage your [crawl budget], as you want to ensure that bots spend their time on valuable content. For instance, you might exclude pages like “Thank You” or login pages that don’t contribute to your site’s SEO.
- Customizing Your Robots.txt: Your robots.txt file should be tailored to meet your specific goals. Depending on your objectives, you can customize it to allow or disallow certain bots and pages accordingly.
3. Optimize your Crawl Budget
Your crawl budget isn’t infinite, so you need to prioritize your important pages for crawling:
- Remove or Canonicalize Duplicates: Eliminate duplicate content or use canonical tags.
- Fix Broken Links: Regularly check for broken links and set up redirects.
- Ensure Crawlability of CSS and JavaScript: Make sure search bots can access these files.
- Monitor Crawl Stats: Keep an eye on your crawl stats for unusual dips or spikes.
- Verify Disallowed Bots and Pages: Ensure any blocked bots or pages are intentionally disallowed.
- Update Your Sitemap: Keep your sitemap current and submit it to webmaster tools.
- Prune Outdated Content: Remove unnecessary or outdated content.
- Manage Dynamic URLs: Watch for dynamic URLs that can inflate your page count.
4. Site Architecture optimization
Your site Architecture is crucial as any well-structured website helps users navigate through the website easily while also helping search engines crawl and index your pages efficiently.
A great way to do this is by organizing your pages into a logical hierarchy, placing the most important ones—like your homepage and key service pages—at the top. This not only makes them more easily accessible but also signals to search engines which pages hold the most value.
In addition to a clear hierarchy, you should use links wisely to connect your pages. Relevant internal links should be connected to related pages as it establishes relationships between your content and helps distribute link equity. For example, a link from a blog post to a related product page not only guides users but also enhances the importance of those pages in the eyes of search engines.
Remember to regularly audit and update your site structure as well. Remove outdated content and ensure all pages are properly linked to maintain an organized architecture.
5. Breadcrumb Menus
Further ways to continue improving your site’s navigation are Breadcrumb Menus as shown below.

These help users retrace their steps on your site and show how the current page they’re on fits within the broader structure of your site
Here’s how to effectively implement them:
- Add Breadcrumbs: This typically appears at the top of your pages, displaying the content hierarchy (e.g., Home > Category > Subcategory > Current Page). Make sure they work!
- Use Clear Labels: Ensure that each breadcrumb link has clear and descriptive labels to help users navigate intuitively.
- Ensure Visibility: Make your breadcrumbs visible and accessible so users can quickly find and use them as needed.
- Utilize Structured Data: Use BreadcrumbList – Schema.org Type markup to help search engines understand your navigation context.
- Monitor User Behavior: Use analytics tools to track user engagement with breadcrumbs and adjust as needed.
6. Establish a Consistent URL Structure
You need to create a consistent URL structure for an enhanced user experience and SEO. Here’s how to establish one:
- Choose Between Subdomains and Subdirectories: Decide whether to use subdomains (e.g., blog.yourwebsite.com) or subdirectories (e.g., yourwebsite.com/blog) for classifying your content. Both have their pros and cons, but consistency is key.
- Create a Logical Hierarchy: Order your URLs in a way that reflects the hierarchy of your content. For example, main categories should be easily identifiable in the URL- example a product page www.yourwebsite.com/products/grooming-brush.
- [Use Descriptive Keywords]: Use relevant keywords that accurately describe the content of the page. This helps with context to users and search engine rankings.
- Keep URLs Short and Simple: Avoid unnecessary words or special characters for clarity. Use lowercase letters to prevent duplicate URL issues. Use dashes to separate words and avoid special characters to ease readability and URL complications.
- Update XML Sitemap: Always submit an XML sitemap after finalizing your URL structure. This provides search engines with a clear overview of your site’s organization.
Create specific guidelines for naming your URLs and apply them consistently throughout your site. This uniformity helps improve site navigation and enhances SEO.
7. Use Pagination
Pagination is the process of dividing content into separate pages or sections, making it easier for users to navigate through large sets of information. It’s often used in blogs, e-commerce sites, and forums where numerous items or posts need to be displayed without overwhelming the user.
For example, instead of showing 800 products on a single page, an e-commerce site might display 10 products per page instead and include navigation links with Rel=“next” and Rel=“prev” Tags to the other pages or have infinite scroll option.
Ensure that each paginated page has a clear and descriptive URL (e.g., www.yourwebsite.com/products?page=2), as it tells search bots which page to crawl next and establishes a clear link structure between your content.
8. Check SEO Log Files
Think of log files as the receipts from a busy restaurant. Each receipt captures essential details, like what was ordered, when it was ordered, and who placed the order. In the same way, log files document every request made to your website, recording the time, date, requested content, and the IP address of the requester, as well as identifying the user agent (the software making the request, such as a search bot).
Log files are important for SEO because they reveal the activity of search bots as they crawl your site, just like receipts show what dishes were popular or if any orders were missed. By analyzing these logs, you can determine which pages were crawled, when they were accessed, and what barriers might be preventing certain pages from being indexed.
By regularly checking your SEO log files, with tools like Screaming Frog, or Google Search Console you can understand how search engines interact with your site, allowing you to make informed adjustments ensuring a more efficient experience for both users and bots.
Rendering Optimization
Rendering is the process where; after crawling a web page, search bots process the page’s content by interpreting and displaying the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Think of it as the bot “seeing” the page as a human would.
A website’s accessibility relies heavily on ease of rendering. Here are essential elements to include in your renderability audit:
- Optimize Page Load Speed: Server slowdowns and errors can block bot access. Fast-loading pages are easier for bots to render fully. Optimizing images and CSS/JavaScript files and leveraging caching techniques can help.
- Check for JavaScript Issues: Google can struggle with JavaScript-heavy sites. Pre-render critical elements or use server-side rendering to ensure bots can access and interpret the content properly.
- Reduce Redirect Chains: Excessive redirects can prevent bots from reaching content effectively and prevent pages from rendering completely. Try to keep redirect chains to a minimum.
- Monitor Server Health: Maintaining a responsive and error-free server is critical for successful rendering. If a page times out or fails due to server errors, search bots may abandon the crawl or disregard important content.
- Use Crawl and Render Analysis Tools: Tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, or DeepCrawl help identify and resolve any render-blocking issues.
Indexability Optimization
Indexability is the ability of search engines to include your web pages in their index. If a page isn’t indexed, it won’t appear in search results, regardless of its content quality.

1. Check for HTTP Errors.
You should monitor your site for any HTTP errors like 404 (Not Found) or 500 (Server Error) on a regular basis as they can block search engines and users from accessing your pages.
Broken links and server issues both disrupt a user’s experience and prevent bots from fully crawling your site. Use tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, or DeepCrawl to scan your pages for these errors:
- 404 Not Found errors are when a page doesn’t exist due to removal or mistyped URLs. Redirect these pages to similar content to retain visitors and avoid broken links that frustrate both users and bots.
- 301 Permanent Redirects are URLs that need to be permanently rerouted to maintain SEO value. However, you should avoid multiple redirect chains as these slow load times and reduce crawl efficiency. For temporary changes, 302 Temporary Redirects can be used, but it should be updated if they become permanent, as they may eventually transfer SEO value to the new page.
- 500 Internal Server Errors often signal server issues, preventing the site from displaying. This can usually be resolved by checking server logs, memory limits, or plugin conflicts. When performing site maintenance, the 503 Service Unavailable code temporarily blocks access the when the server is overloaded or under maintenance (In this instance make sure provide a clear message of your site’s expected return). Errors like 502 Bad Gateway and 504 Gateway Timeout usually stem from miscommunication between servers, so checking server configurations is key to prevent delays in page access.
- 403 Forbidden errors indicate server is refusing access to a page. Verify permissions and adjust settings as needed to ensure that both bots and users have access to publicly intended pages.
Make sure to Audit the redirects by reviewing and analyzing them on your website to ensure they function correctly and efficiently. Some redirects create chains or loops, where multiple redirects point to one another. You want to make sure users and search engines can access your content without any unnecessary delays.
2. Unblock Search Bots.
Unblocking search bots ensures they can access and crawl your prioritized content pages. When search engines send bots to your website, they follow instructions in a robots.txt file, which may block or allow certain parts of your site. If your key pages are accidentally blocked in this file, search engines won’t crawl them, which results in reduced visibility and rankings.
Using tools like Google’s robots.txt tester in Search Console can help you check if any URLs are blocked and adjust the file to grant bots access. The Google Search Console’s Inspect tool can help pinpoint reasons for page restrictions.
Remember to only use blocking or disallowed directives on pages that you don’t need to appear in search results.
3. Remove Duplicate Content.
Duplicate content occurs when identical or substantially similar content appears on multiple pages of your site or across different sites causing confusion, making it difficult for search engines to determine which version of the content to index or rank.
Simple ways to prevent this are by using canonical tags to specify the preferred version of a page and 301 redirects to guide visitors and search engines from the duplicate page to the original content.
You can use the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console to show you the Google-selected canonical URL.
4. Ensure Mobile Responsiveness.
Approximately 60.4%of global web traffic originates from mobile devices which emphasizes the importance of ensuring that your website is mobile-responsive. A responsive design allows your website to smoothly adapt to various screen sizes, making navigation easier and content more accessible for visitors. Tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test and PageSpeed Insights can provide valuable insights to assess and optimize your site’s mobile performance.
5. Implement Structured Data
Incorporating structured data is essentially giving search engines a clear manual to your website’s content.
Using structured data markup gives specified information about your pages to search engines which helps them understand the context and relevance of your content. This can enhance your search listings with rich snippets, which often lead to higher click-through rates.
Here are some simple steps:
- Select the Right Schema: Schema.org website is one of the best sources to find the correct type of structured data for your pages e.g. whether it’s for personal profiles, articles, products, events, or reviews.
- Add Markup to Your Pages: Jason-LD is recommended by Google for its ease of use and separation from HTML. Place it in the
<head>section or at the end of your HTML document.
For example, a JSON-LD script for a blog post might look like this:
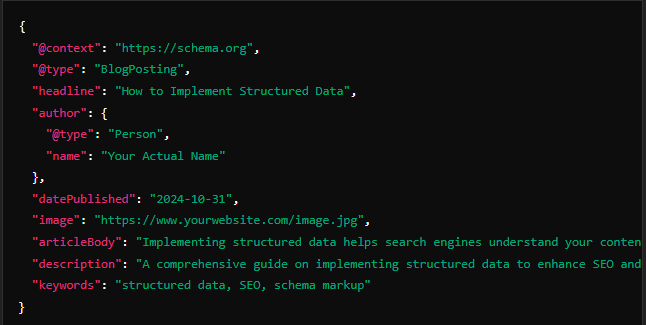
- Test and Monitor: Use tools like Google’s Rich Results Test or Schema Markup validator to assure your structured data is correctly implemented and rich snippets are displaying correctly.
6. Check for Orphan Pages.
Orphan pages are web pages that don’t have any internal links pointing to them from other pages on your site. This lack of connectivity makes it challenging for both users and search engines to discover and access these pages, reducing their visibility and indexing.
To address this, you should link them to related content within your site to help users and search engine bots can easily find and understand their importance.
Rankability Optimization
This is all about the quality and the effectiveness of your optimization strategies to increase your web page’s potential to secure a high position in search engine results pages (SERPs).
While you might already be familiar with how to enhance rankings from a technical SEO perspective, remember that rankability encompasses both on-page and off-page elements that work in harmony to create an SEO-friendly site. Let’s explore some of these elements:
- Content Quality: High-quality, relevant content that addresses user intent tends to rank better. Search engines prioritize content that is informative, engaging, and useful. Additionally, organizing your content into clusters where you relate pieces of content together, makes it easier for search bots to find, crawl, and index all your pages on a particular topic.
- Internal and External Linking: The quantity and quality of links pointing to a page significantly affect its rankability. Links are vital for helping search bots understand how your page fits within the broader context of a query. Pages with authoritative backlinks are viewed more favorably by search engines and assists users in finding relevant pages on your site.
- Backlink Quality: Backlinks—links from other sites pointing to yours— are necessary for authority as they signal to bots that your page is high-quality and credible. Essentially, they are a vote of confidence for your content. However, getting backlinks from any website is not the goal. The quality of your backlinks matters significantly as links from spammy websites indicate your site may be spam as well.
Clickability Optimization
Clickability refers to the likelihood that users will click on a search result when it appears in search engine results pages (SERPs) so you need to improve your link’s appearance to stand out.
So, let’s cover a few ways to encourage clicks:
- Optimize for Featured Snippets: When you structure your content to answer common questions clearly and concisely, it can help you capture featured snippets, which are highlighted at the top of search results and often lead to higher click-through rates.
- Target SERP Features: In addition to featured snippets, aim to obtain other SERP features like Knowledge Panels, People Also Ask boxes, and Local Packs. Securing these features increases your visibility and can draw more clicks.
- Optimize for Google Discover: Optimize your content for Google Discover by creating visually appealing and engaging content that resonates with your target audience’s interests. Tailor your headlines and images to align with user interests and current trends to maximize visibility.
- Craft Compelling Meta Titles and Descriptions: Make sure your meta titles and descriptions are captivating and accurately reflect your content. Strong, clear calls to action are necessary to boost click-through rates.
- Use Schema Markup: As mentioned earlier, structured data enhances how your page appears in search results. Schema markup enhances Rich snippets-additional information displayed alongside your link such as ratings or prices, helping your listing to stand out more.
- Leverage Social Proof and Reviews: Add user reviews or testimonials in your content to build trust. Highlighting positive feedback can encourage clicks from skeptical users enhancing credibility.
Remember…
Incorporating these technical tactics into your SEO strategy is essential for maximizing your search performance. By conducting regular technical SEO audits, you can identify actionable steps that significantly improve your site’s visibility.
While addressing issues like indexing and broken links can yield immediate benefits, it’s important to balance these efforts with a focus on enhancing your content and building quality links.
Ultimately, a well-rounded approach of Technical SEO, on-page SEO, and off-page SEO will lead to the best results in search engine rankings.
If there’s anything else you’d like for me to touch on, let me know in the comments below!


